Treatment of Lymphedema ③
Surgery for Lymphedema 2: Lymph Node Grafting
In the treatment of lymphedema, it has been found that for cases where the lymphatic vessels have degenerated and the lymphedema has worsened, combining conservative treatment with surgical treatment has been found to potentially reduce the symptoms of lymphedema, slow down the rate of worsening, and reduce cellulitis (infection).
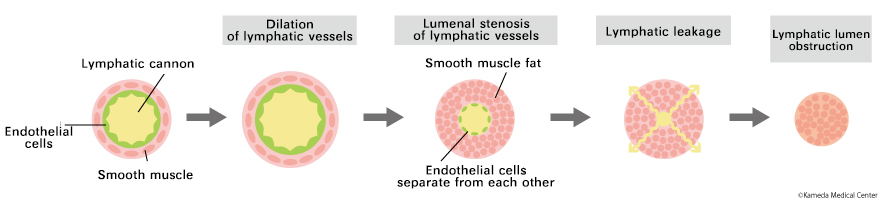
Lymphatic venous anastomosis, which is the least invasive method of surgical treatments, is more effective when there are many lymphatic vessels with less than moderate degeneration and a low degree of stenosis as shown on the left side of the figure below. On the other hand, in cases where the majority of the lymphatic vessels are narrowed or blocked due to degeneration, as shown on the right side of the figure below, the effect of the surgery will be low or almost non-existent.
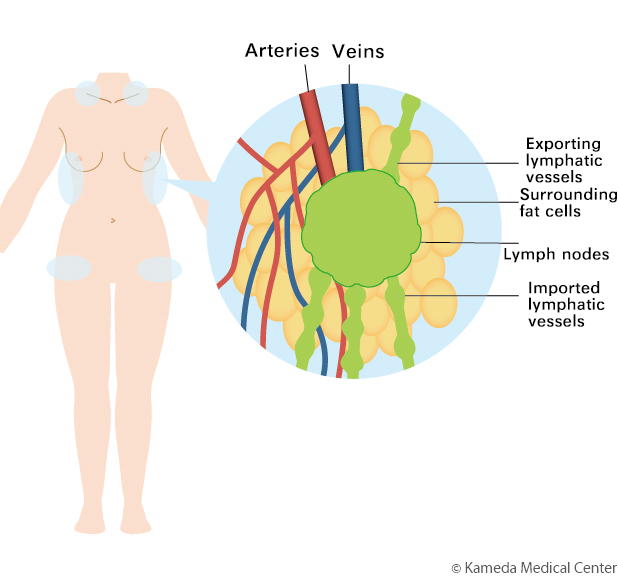
そのようなリンパ管の変性が進んでしまっているリンパ浮腫の症例に対しては、「リンパ節移植術」という方法があります。
この手術は、まず、健常部位(鎖骨周囲、側胸部、鼡径部など)にあるリンパ節とその周囲の脂肪組織を、それを栄養する血管と一緒に採取してきます。
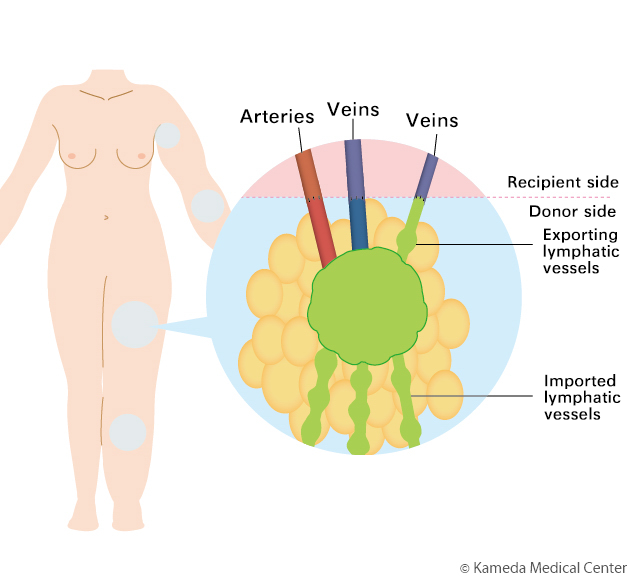
Next, the harvested lymph node(s) and surrounding tissues (donor side) are transplanted to the site of lymphedema where severe lymphoid degeneration is observed (recipient side), and the blood vessels (arteries and veins) feeding the lymph node(s) and ones of the graft bed are anastomosed under a microscope. If the exporting lymphatic vessel of the node to be transplanted can be identified, it is anastomosed with the vein on the recipient side.
The mechanism by which lymph node transplantation is effective against lymphedema is as follows:
- ・Lymph nodes themselves have a pumping action that collects and drains lymph; at the same time, there is a physiological “lymphatic-venous anastomosis” within the nodes that allows stagnant lymph to drain through these functions.
- Lymph angiogenesis factors are released from the transplanted lymph node, forming a new lymphatic channel and improving lymphatic stasis.
As with lymphatic-venous anastomosis, a reduction in circumference, cellulitis, and subjective symptoms (heaviness, numbness, pain, etc.) can be expected after the procedure, but it should be noted that the procedure is slightly more invasive than the former, and it takes longer (six months to a year or more) for the effects to appear. It should also be noted that it is difficult to reduce fat that has already grown due to the worsening of lymphedema via this technique, and that a separate method called liposuction would be needed to remove the grown fat.

林明辰Akitatsu Hayashi
龟田总合医院/龟田京桥诊所
淋巴水肿中心 院长
世界上首次宣布使用超音波与干涉断层扫描(OCT)的尖端淋巴管形成技术。我们专注于使用此技术传播更有效的淋巴水肿手术。



